
“On-Premises vs Cloud: Which is the right fit for your business?” This question is on the minds of business leaders and decision-makers everywhere.
On-premise infrastructure offers robust security and control, while cloud solutions provide unparalleled scalability and flexibility. This ongoing debate deserves a clear answer, and chances are, you’re here to find the right solution for your business needs.
The trend is clear: Nearly 48% of companies plan to migrate half of their applications to the cloud, with 20% aiming for a full migration. However, many businesses still rely on on-premise infrastructure for their critical operations.
Regardless of your choice, building your infrastructure on a well-thought-out hosting strategy is essential. Doing so will help you avoid over-investment, frequent downtime, and limited scalability. To make the right choice, consider key factors such as security, budget, scalability, etc.
Check out our blog to help simplify your decision-making process.
What is the On-premises model?
The On-premises model involves deploying and managing software within an organization’s infrastructure instead of cloud-based solutions. In this setup, the software is installed and operates on servers that are owned, maintained, and housed by the organization itself.
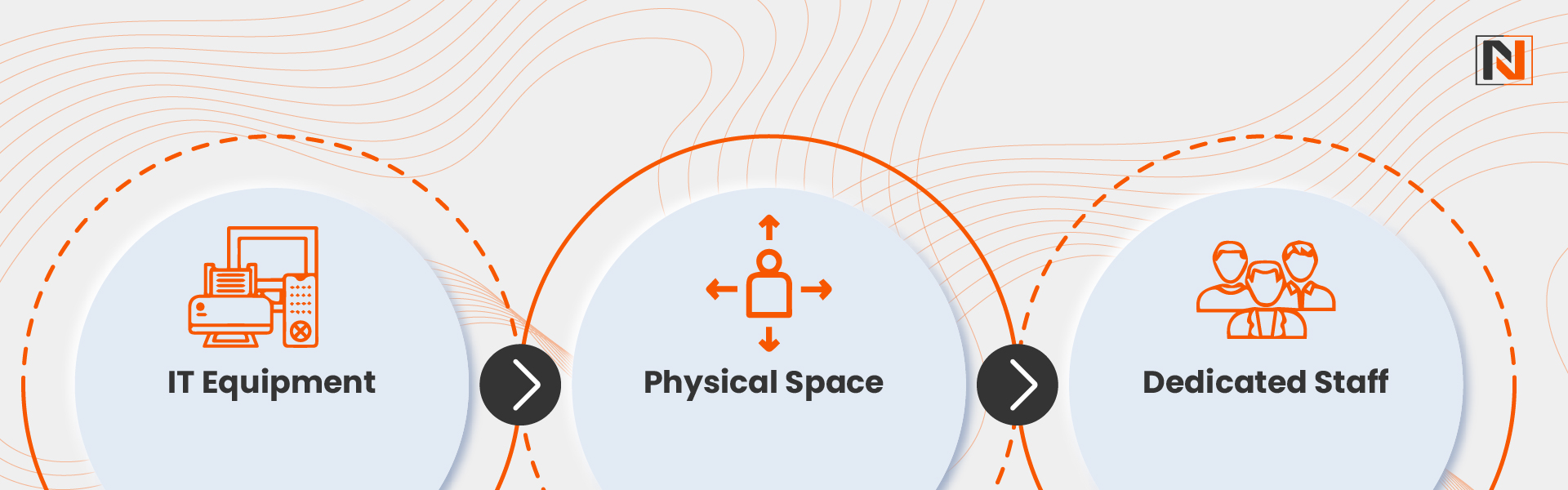
Key requirements for this model include:
- IT Equipment: This includes storage servers, CPUs, routers, server racks, cooling units, and a reliable power source to ensure smooth, continuous operations.
- Physical Space: A dedicated area is needed to house the servers, ensuring they are kept in optimal conditions to avoid overheating and other potential problems.
- Dedicated Staff: Skilled personnel are responsible for maintaining, securing, and monitoring the system to ensure its efficiency, uphold security protocols, and address any issues or malfunctions as they arise.
The On-premises model is particularly attractive to businesses that value control and customization, such as those in industries like finance, healthcare, and government, where strict data security and compliance regulations are paramount.
These organizations often prefer direct oversight of their data and system configurations. Although this approach requires significant upfront costs for hardware and software, it also demands a comprehensive strategy for disaster recovery and minimizing downtime.
What is the Cloud model?
Cloud computing involves accessing computing services such as storage, processing, and networking via the internet, with third-party Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and IBM Cloud handling the infrastructure.
By adopting cloud solutions, businesses and individuals can minimize their reliance on physical hardware, as the cloud provider manages everything from databases to machine learning tools. This reduces the need for in-house software management.
Cloud adoption offers benefits such as scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency. Rather than making large upfront investments in hardware, users can pay for services on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis. However, users must trust these providers to maintain security, compliance, and reliable uptime.
Did You Know?
According to Statista, IT professionals worldwide estimate that their organizations have a nearly 50/50 distribution, with 50% on-site servers and 50% cloud-hosted servers.
Gartner predicts that the cloud technology market will surpass $1 trillion by 2027, marking the rise of the cloud-first era.
On-Premises vs Cloud: Key Differences
When comparing On-Premises and Cloud solutions, several key differences exist. Here’s a breakdown of the main distinctions:
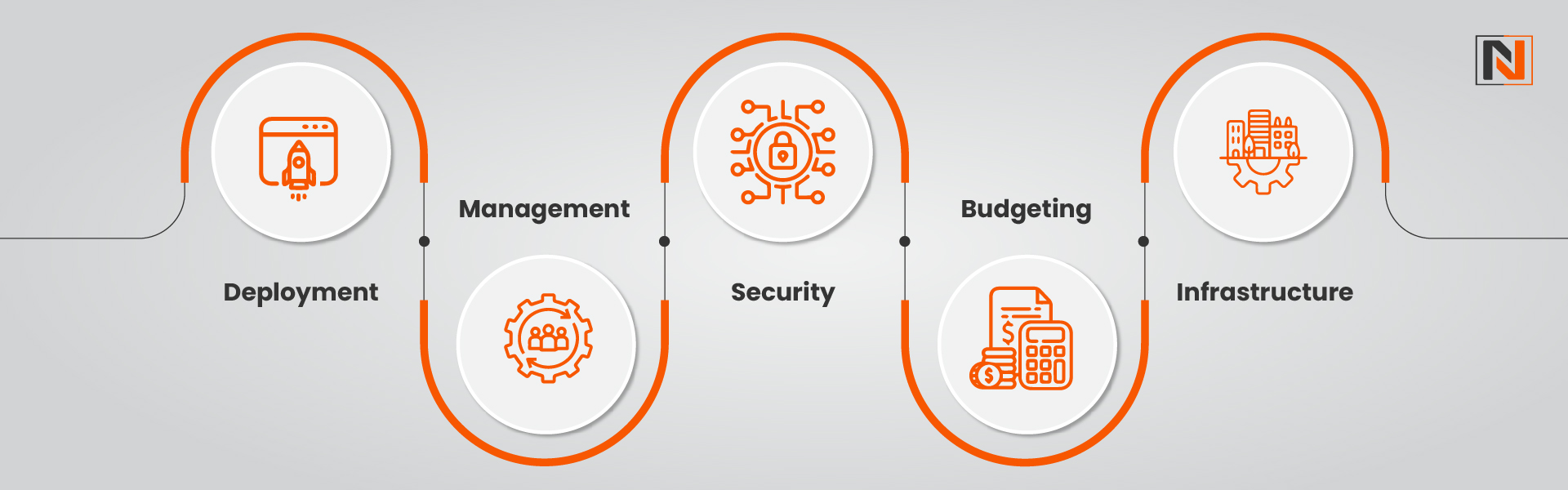
1. Deployment
Deploying software is similar in both cloud and on-premises environments, but hardware deployment varies greatly. For on-premises setups, IT teams must order, rack, network, and provision additional servers for the data center. In contrast, cloud environments offer a simpler process, and servers can be spun up with just a click or a few commands.
2. Management
Cloud providers handle much of the management work, allowing users to focus mainly on monitoring and adjusting settings through management dashboards or software tools. On-premises systems require active maintenance, including hardware upkeep, network management, power control, and building maintenance.
3. Security
In the cloud, security is shared between the provider and the user. The provider secures the infrastructure, while users must ensure data and applications are properly configured and protected. On-premises environments, IT teams are fully responsible for handling software patches, operating system upgrades, and security configurations for applications and networks.
4. Budgeting
Cloud services are more cost-effective, as users can pay only for the resources they use and scale down when needed. However, users must monitor cloud usage to avoid unexpected costs. On-premises infrastructure comes with a fixed price, but inefficient resource usage can lead to financial waste. Expanding capacity through additional hardware can also take years to reach a point of cost-effectiveness.
5. Infrastructure
Cloud providers invest heavily in robust infrastructure to support high availability, quick response times, and scalable resources. They manage user access to this infrastructure. On-premises, IT teams own and control the infrastructure but are constrained by what they can afford or acquire.
Must Read – How to Choose the Right Cloud Service for Your Business Needs
On-Premises vs Cloud: How to Choose the Right Infrastructure?
Selecting the right IT infrastructure for your business involves thoughtful planning and aligning it with your cloud strategy. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed choice:

1. Understand Your Business Needs
Before selecting any infrastructure, it’s crucial to understand your business clearly. Identify your requirements regarding user needs, workloads, performance, scalability, and storage. Choose mission-critical applications that can support daily operations and ensure the safety and availability of your data. Consider your business’s current situation, future goals, and growth potential.
2. Review Your Existing Infrastructure
Take time to evaluate your current infrastructure. Determine what additional resources or upgrades are necessary. If opting for on-premises solutions, assess the skills, costs, and time required for your IT team to get up to speed. Review the lifecycle of your hardware and software and how well they can keep up with rapidly changing technology. Identify any gaps that could hinder your transition to a more advanced infrastructure.
3. Comply with Regulatory and Legal Requirements
Your industry’s regulatory requirements may influence how and where you store and access data. Non-compliance could lead to hefty fines and disruptions. Whether opting for Cloud or on-premises, ensure you understand the data governance rules specific to your sector. Certain data may need the strict control offered by on-premises solutions, while Cloud systems might be ideal for others due to their enhanced security features.
4. Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Consider both direct and indirect costs for on-premises versus Cloud solutions. On-premises typically involve servers, software licenses, maintenance, power, cooling, and staffing expenses. On the other hand, cloud solutions include service costs, data transfer fees, and potential downtime. Compare these costs to find the most cost-effective solution.
5. Focus on Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud infrastructure offers great scalability, making it a perfect option if your business experiences fluctuating demand or rapid growth. On-premises might be more suitable for steady workloads. Evaluate the flexibility each option provides in meeting your evolving business needs.
6. Compare Vendor Options
If you are considering Cloud or hybrid solutions, research potential vendors with a proven track record, expertise, and credibility. List reliable options and compare them in terms of costs, features, customer support, and compatibility with your existing systems. Choose a vendor that can adapt to your future needs, ensuring your solution grows with your business and avoids needing another switch sooner than expected.
7. Finalize the Agreement and Start Development
Once you’ve made your decision, formalize the agreement with the chosen vendor by signing the Service Level Agreement (SLA). This ensures both parties are aligned on performance, uptime, support, and other key service details. After the SLA is in place, you can proceed with infrastructure development.
You can either build an in-house team or hire cloud consulting services (if choosing Cloud). Ensure your development team is aligned with the infrastructure strategy to guarantee smooth implementation. Set clear objectives, allocate resources wisely, and monitor progress to ensure a successful transition.
Conclusion
In the end, the decision comes down to balancing control and flexibility. On-premises models are ideal for businesses that need strict data control and compliance, while cloud solutions are perfect for those seeking scalability and cost-efficiency. Assess your business’s unique requirements to ensure you pick the best model for the future. For clear guidance on which model suits your business, contact Nirvana Lab today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between On-premises and Cloud infrastructure?
On-premises infrastructure manages software and hardware within an organization’s facilities, offering full control but requiring significant upfront costs and maintenance. Cloud infrastructure provides services over the internet, managed by third-party providers, offering scalability and cost-effectiveness but requiring trust in the provider for security and uptime.
Which model offers better security, On-premises or Cloud?
On-premises systems provide full control over security but require dedicated IT staff for maintenance and patching. In the Cloud, security is shared between the provider and the user, where the provider manages infrastructure security, and users are responsible for securing their data and applications.
Which model is more cost-effective, On-premises or Cloud?
Cloud computing is generally more cost-effective due to its pay-as-you-go model, which allows businesses to scale up or down based on needs. On-premises solutions require significant upfront investments in hardware, software, and staff and may result in financial waste if resources aren’t used efficiently.
What factors should I consider when choosing between On-premises and Cloud?
Consider your business’s scalability, flexibility, security, cost, and compliance needs. Review your current infrastructure, assess regulatory requirements, and compare the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for both models to determine the best fit for your business.
Can I combine On-premises and Cloud models?
Yes, a hybrid model can be combined with On-premises and Cloud solutions. This approach allows businesses to maintain critical operations in-house while leveraging the cloud for scalability and flexibility. It’s ideal for businesses that need a balance of control and growth potential.

“On-Premises vs Cloud: Which is the right fit for your business?” This question is on the minds of business leaders and decision-makers everywhere.
On-premise infrastructure offers robust security and control, while cloud solutions provide unparalleled scalability and flexibility. This ongoing debate deserves a clear answer, and chances are, you’re here to find the right solution for your business needs.
The trend is clear: Nearly 48% of companies plan to migrate half of their applications to the cloud, with 20% aiming for a full migration. However, many businesses still rely on on-premise infrastructure for their critical operations.
Regardless of your choice, building your infrastructure on a well-thought-out hosting strategy is essential. Doing so will help you avoid over-investment, frequent downtime, and limited scalability. To make the right choice, consider key factors such as security, budget, scalability, etc.
Check out our blog to help simplify your decision-making process.
What is the On-premises model?
The On-premises model involves deploying and managing software within an organization’s infrastructure instead of cloud-based solutions. In this setup, the software is installed and operates on servers that are owned, maintained, and housed by the organization itself.

Key requirements for this model include:
- IT Equipment: This includes storage servers, CPUs, routers, server racks, cooling units, and a reliable power source to ensure smooth, continuous operations.
- Physical Space: A dedicated area is needed to house the servers, ensuring they are kept in optimal conditions to avoid overheating and other potential problems.
- Dedicated Staff: Skilled personnel are responsible for maintaining, securing, and monitoring the system to ensure its efficiency, uphold security protocols, and address any issues or malfunctions as they arise.
The On-premises model is particularly attractive to businesses that value control and customization, such as those in industries like finance, healthcare, and government, where strict data security and compliance regulations are paramount.
These organizations often prefer direct oversight of their data and system configurations. Although this approach requires significant upfront costs for hardware and software, it also demands a comprehensive strategy for disaster recovery and minimizing downtime.
What is the Cloud model?
Cloud computing involves accessing computing services such as storage, processing, and networking via the internet, with third-party Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and IBM Cloud handling the infrastructure.
By adopting cloud solutions, businesses and individuals can minimize their reliance on physical hardware, as the cloud provider manages everything from databases to machine learning tools. This reduces the need for in-house software management.
Cloud adoption offers benefits such as scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency. Rather than making large upfront investments in hardware, users can pay for services on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis. However, users must trust these providers to maintain security, compliance, and reliable uptime.
Did You Know?
According to Statista, IT professionals worldwide estimate that their organizations have a nearly 50/50 distribution, with 50% on-site servers and 50% cloud-hosted servers.
Gartner predicts that the cloud technology market will surpass $1 trillion by 2027, marking the rise of the cloud-first era.
On-Premises vs Cloud: Key Differences
When comparing On-Premises and Cloud solutions, several key differences exist. Here’s a breakdown of the main distinctions:

1. Deployment
Deploying software is similar in both cloud and on-premises environments, but hardware deployment varies greatly. For on-premises setups, IT teams must order, rack, network, and provision additional servers for the data center. In contrast, cloud environments offer a simpler process, and servers can be spun up with just a click or a few commands.
2. Management
Cloud providers handle much of the management work, allowing users to focus mainly on monitoring and adjusting settings through management dashboards or software tools. On-premises systems require active maintenance, including hardware upkeep, network management, power control, and building maintenance.
3. Security
In the cloud, security is shared between the provider and the user. The provider secures the infrastructure, while users must ensure data and applications are properly configured and protected. On-premises environments, IT teams are fully responsible for handling software patches, operating system upgrades, and security configurations for applications and networks.
4. Budgeting
Cloud services are more cost-effective, as users can pay only for the resources they use and scale down when needed. However, users must monitor cloud usage to avoid unexpected costs. On-premises infrastructure comes with a fixed price, but inefficient resource usage can lead to financial waste. Expanding capacity through additional hardware can also take years to reach a point of cost-effectiveness.
5. Infrastructure
Cloud providers invest heavily in robust infrastructure to support high availability, quick response times, and scalable resources. They manage user access to this infrastructure. On-premises, IT teams own and control the infrastructure but are constrained by what they can afford or acquire.
Must Read – How to Choose the Right Cloud Service for Your Business Needs
On-Premises vs Cloud: How to Choose the Right Infrastructure?
Selecting the right IT infrastructure for your business involves thoughtful planning and aligning it with your cloud strategy. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed choice:

1. Understand Your Business Needs
Before selecting any infrastructure, it’s crucial to understand your business clearly. Identify your requirements regarding user needs, workloads, performance, scalability, and storage. Choose mission-critical applications that can support daily operations and ensure the safety and availability of your data. Consider your business’s current situation, future goals, and growth potential.
2. Review Your Existing Infrastructure
Take time to evaluate your current infrastructure. Determine what additional resources or upgrades are necessary. If opting for on-premises solutions, assess the skills, costs, and time required for your IT team to get up to speed. Review the lifecycle of your hardware and software and how well they can keep up with rapidly changing technology. Identify any gaps that could hinder your transition to a more advanced infrastructure.
3. Comply with Regulatory and Legal Requirements
Your industry’s regulatory requirements may influence how and where you store and access data. Non-compliance could lead to hefty fines and disruptions. Whether opting for Cloud or on-premises, ensure you understand the data governance rules specific to your sector. Certain data may need the strict control offered by on-premises solutions, while Cloud systems might be ideal for others due to their enhanced security features.
4. Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Consider both direct and indirect costs for on-premises versus Cloud solutions. On-premises typically involve servers, software licenses, maintenance, power, cooling, and staffing expenses. On the other hand, cloud solutions include service costs, data transfer fees, and potential downtime. Compare these costs to find the most cost-effective solution.
5. Focus on Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud infrastructure offers great scalability, making it a perfect option if your business experiences fluctuating demand or rapid growth. On-premises might be more suitable for steady workloads. Evaluate the flexibility each option provides in meeting your evolving business needs.
6. Compare Vendor Options
If you are considering Cloud or hybrid solutions, research potential vendors with a proven track record, expertise, and credibility. List reliable options and compare them in terms of costs, features, customer support, and compatibility with your existing systems. Choose a vendor that can adapt to your future needs, ensuring your solution grows with your business and avoids needing another switch sooner than expected.
7. Finalize the Agreement and Start Development
Once you’ve made your decision, formalize the agreement with the chosen vendor by signing the Service Level Agreement (SLA). This ensures both parties are aligned on performance, uptime, support, and other key service details. After the SLA is in place, you can proceed with infrastructure development.
You can either build an in-house team or hire cloud consulting services (if choosing Cloud). Ensure your development team is aligned with the infrastructure strategy to guarantee smooth implementation. Set clear objectives, allocate resources wisely, and monitor progress to ensure a successful transition.
Conclusion
In the end, the decision comes down to balancing control and flexibility. On-premises models are ideal for businesses that need strict data control and compliance, while cloud solutions are perfect for those seeking scalability and cost-efficiency. Assess your business’s unique requirements to ensure you pick the best model for the future. For clear guidance on which model suits your business, contact Nirvana Lab today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between On-premises and Cloud infrastructure?
On-premises infrastructure manages software and hardware within an organization’s facilities, offering full control but requiring significant upfront costs and maintenance. Cloud infrastructure provides services over the internet, managed by third-party providers, offering scalability and cost-effectiveness but requiring trust in the provider for security and uptime.
Which model offers better security, On-premises or Cloud?
On-premises systems provide full control over security but require dedicated IT staff for maintenance and patching. In the Cloud, security is shared between the provider and the user, where the provider manages infrastructure security, and users are responsible for securing their data and applications.
Which model is more cost-effective, On-premises or Cloud?
Cloud computing is generally more cost-effective due to its pay-as-you-go model, which allows businesses to scale up or down based on needs. On-premises solutions require significant upfront investments in hardware, software, and staff and may result in financial waste if resources aren’t used efficiently.
What factors should I consider when choosing between On-premises and Cloud?
Consider your business’s scalability, flexibility, security, cost, and compliance needs. Review your current infrastructure, assess regulatory requirements, and compare the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for both models to determine the best fit for your business.
Can I combine On-premises and Cloud models?
Yes, a hybrid model can be combined with On-premises and Cloud solutions. This approach allows businesses to maintain critical operations in-house while leveraging the cloud for scalability and flexibility. It’s ideal for businesses that need a balance of control and growth potential.
