Businesses are increasingly relying on cloud computing to drive –
Innovation
Scalability
Operational Efficiency
However, with the growing complexity of cloud environments, decision-makers are faced with a critical question: What is the difference between Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud, and which cloud strategy is best for my business?
This blog will explore the nuances of Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud strategies, their benefits, challenges, and how to choose the right approach for your organization. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to align your cloud strategy with your business goals.
Understanding Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud
Before diving into the comparison, let’s define the two strategies:
What is Hybrid Cloud?
A Hybrid Cloud strategy combines on-premises infrastructure (private cloud) with public cloud services, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This approach provides businesses with greater flexibility, enabling them to keep sensitive data on-premises while leveraging the scalability of public clouds for less critical workloads.
What is Multi-Cloud?
A Multi-Cloud strategy involves using multiple public cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud) to meet different business needs. Organizations adopt this approach to avoid vendor lock-in, optimize costs, and leverage the unique strengths of each cloud provider. While both strategies aim to enhance business agility, they differ in their architecture, use cases, and management complexities. Let’s break down the key differences.
Hybrid Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud: Key Differences
Both Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud involve using multiple cloud environments, but they serve different purposes. Here’s a breakdown of their key differences:
| Feature | Hybrid Cloud | Multi-Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A combination of private and public clouds that work together. | A strategy that uses multiple cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, etc.) for different services. |
| Infrastructure | Integrates private and public cloud environments to function as a unified system. | Uses multiple public cloud providers, often without integrating them. |
| Purpose | Optimized for flexibility, scalability, and security, allowing sensitive data to remain on-premises while utilizing public cloud resources. | Designed to avoid vendor lock-in, improve redundancy, and use best-of-breed cloud services. |
| Workload Distribution | Workloads are distributed between private and public clouds based on security, performance, and cost factors. | Workloads are distributed across multiple cloud providers, often for cost optimization and performance enhancement. |
| Security & Compliance | Provides more control over security and compliance by keeping sensitive workloads in a private cloud. | Security depends on multiple cloud providers, requiring strong governance and management strategies. |
| Cost Management | Can be more cost-effective by balancing private infrastructure costs with public cloud flexibility. | May reduce costs by leveraging competitive pricing from multiple providers. |
| Integration | Requires strong integration between private and public cloud environments. | May lack deep integration between different cloud platforms. |
Which Cloud Strategy is Best for Your Business?
Choosing between Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud depends on your organization’s unique needs, goals, and constraints. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Data Sensitivity and Compliance
If your business handles highly sensitive data or operates in a regulated industry, a Hybrid Cloud strategy may be more suitable. It allows you to keep critical data on-premises while still benefiting from the scalability of public clouds.
On the other hand, if compliance requirements vary across regions or workloads, a Multi-Cloud approach can help you select providers that meet specific regulatory standards.
MUST KNOW TRENDS - Top Cloud Computing Trends Defining Business Success in 2025
2. Workload Requirements
Consider the nature of your workloads. For example:
Hybrid Cloud is ideal for applications that require low latency or need to run close to on-premises systems.
Multi-Cloud is better for workloads that can benefit from the unique capabilities of different cloud providers, such as AI/ML, big data analytics, or IoT.
A MUST READ - What is a Multi Cloud Strategy?
3. Cost Management
Evaluate your budget and cost optimization goals. A Hybrid Cloud strategy can help you maximize existing infrastructure investments, while a Multi-Cloud approach allows you to shop around for the best pricing and avoid over-reliance on a single provider.
4. Vendor Lock-In Concerns
If avoiding vendor lock-in is a priority, Multi-Cloud is the way to go. It gives you the flexibility to switch providers or distribute workloads across multiple platforms. However, if you’re comfortable with a single provider and prioritize seamless integration, Hybrid Cloud might be a better fit.
5. Operational Expertise
Managing a Hybrid Cloud environment requires expertise in integrating on-premises and public cloud systems. In contrast, a Multi-Cloud strategy demands proficiency in multiple cloud platforms. Assess your team’s skills and consider investing in training or managed services to bridge any gaps.
DID YOU KNOW
The global cloud computing market is projected to expand from USD 626.4 billion in 2023 to USD 1,266.4 billion by 2028, experiencing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.1%.
How to Choose Between Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud
Still unsure which strategy is right for your business? Follow these steps to make an informed decision:
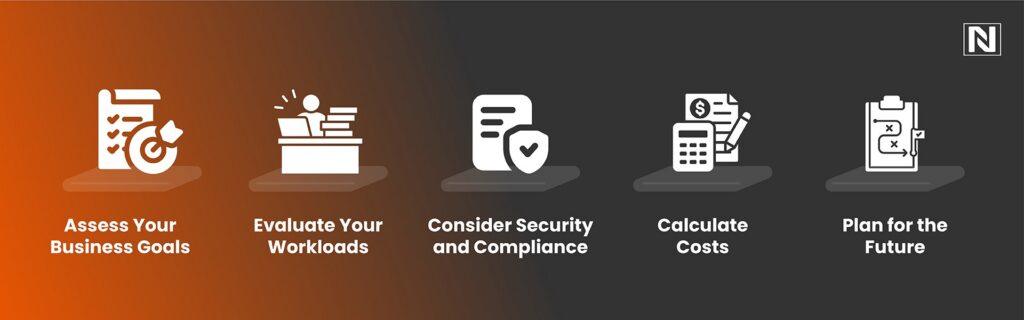
- Assess Your Business Goals: Align your cloud strategy with your organization’s long-term objectives. Are you looking to innovate, reduce costs, or improve scalability?
- Evaluate Your Workloads: Analyze your applications and data to determine which workloads are best suited for on-premises, public, or multi-cloud environments.
- Consider Security and Compliance: Identify any regulatory requirements or security concerns that may influence your decision.
- Calculate Costs: Compare the total cost of ownership (TCO) for each strategy, including infrastructure, management, and potential savings.
- Plan for the Future: Choose a strategy that can adapt to your evolving needs and support future growth.
DON’T MISS THIS BLOG – Why Move to the Cloud? 10 Compelling Reasons for Cloud Migration
Real-World Examples

1. Hybrid Cloud
A global financial institution uses a Hybrid Cloud strategy to store sensitive customer data on-premises while leveraging public cloud services for data analytics and customer-facing applications. This approach ensures compliance with strict regulations while enabling innovation.
2. Multi-Cloud
An e-commerce company adopts a Multi-Cloud strategy to distribute its workloads across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. By doing so, it avoids vendor lock-in, optimizes costs, and ensures high availability during peak shopping seasons.
Final Thoughts
The decision between Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Both strategies offer unique advantages and challenges, and the best choice depends on your business’s specific needs and goals.
If you’re still asking, “Which cloud strategy is best for my business?”, start by evaluating your workloads, security requirements, and long-term objectives. Whether you choose Hybrid Cloud, Multi-Cloud, or a combination of both, the key is to align your cloud strategy with your business priorities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the key difference between Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud?
Hybrid Cloud integrates private and public cloud environments, while Multi-Cloud involves using multiple public cloud providers without necessarily integrating them.
Which cloud strategy is better for cost optimization?
Multi-Cloud helps optimize costs by leveraging competitive pricing from different providers, while Hybrid Cloud balances private infrastructure costs with public cloud scalability.
How do I choose between Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud for my business?
Consider factors like data sensitivity, compliance needs, workload distribution, cost management, and vendor lock-in concerns to determine the best fit.
What are the security implications of Hybrid Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud?
Hybrid Cloud provides greater control over security by keeping sensitive data on-premises, while Multi-Cloud requires strong governance to manage security across multiple providers.
How does Nirvana Lab support businesses with Hybrid and Multi-Cloud strategies?
Nirvana Lab offers tailored cloud solutions, helping businesses optimize infrastructure, improve security, and streamline cloud management for both Hybrid and Multi-Cloud environments.
